### 2021.12.23
최근접 이웃(K-Nearest Neighbor)
- 특별한 예측 모델 없이 가장 가까운 데이터 포인트를 기반으로 예측을 수행하는 방법
- 분류와 회귀 모두 지원

import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import multiprocessing
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use(['seaborn-whitegrid'])
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier, KNeighborsRegressor
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris, load_breast_cancer
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston, fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_validate, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline, Pipeline
K 최근접 이웃 분류
- 입력 데이터 포인트와 가장 가까운 k개의 훈련 데이터 포인트가 출력
- k개의 데이터 포인트 중 가장 많은 클래스가 예측 결과
붓꽃 데이터
#In[]
iris = load_iris()
iris_df = pd.DataFrame(data=iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
iris_df['Target'] = iris.target
iris_df
#Out[]
#In[]
X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2)
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_scale = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_scale = scaler.transform(X_test)
model = KNeighborsClassifier()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
#Out[]
KNeighborsClassifier()데이터 전처리전 점수
#In[]
print("학습 데이터 점수 : {}".format(model.score(X_train, y_train)))
print("평가 데이터 점수 : {}".format(model.score(X_test, y_test)))
학습 데이터 점수 : 0.9583333333333334
평가 데이터 점수 : 1.0데이터 전처리후 점수
#In[1]
model = KNeighborsClassifier()
model.fit(X_train_scale, y_train)
#Out[1]
KNeighborsClassifier()
#In[2]
print("학습 데이터 점수 : {}".format(model.score(X_train_scale, y_train)))
print("평가 데이터 점수 : {}".format(model.score(X_test_scale, y_test)))
#Out[2]
학습 데이터 점수 : 0.9583333333333334
평가 데이터 점수 : 0.9666666666666667#In[]
cross_validate(estimator=KNeighborsClassifier(),
X=X, y=y,
cv=5,
n_jobs=multiprocessing.cpu_count(),
verbose=True)
#Out[]
{'fit_time': array([0.00156212, 0.00154233, 0.00200725, 0.00164413, 0.00190806]),
'score_time': array([0.004287 , 0.00399184, 0.00413203, 0.00383401, 0.00303102]),
'test_score': array([0.96666667, 1. , 0.93333333, 0.96666667, 1. ])}#In[]
param_grid = [{'n_neighbors' : [3,5,7],
'weights' : ['uniform','distance'],
'algorithm' : ['ball_tree', 'kd_tree', 'brute']}]
gs = GridSearchCV(estimator = KNeighborsClassifier(),
param_grid = param_grid,
n_jobs=multiprocessing.cpu_count(),
verbose=True)
gs.fit(X,y)
#Out[]
Fitting 5 folds for each of 18 candidates, totalling 90 fits
GridSearchCV(estimator=KNeighborsClassifier(), n_jobs=4,
param_grid=[{'algorithm': ['ball_tree', 'kd_tree', 'brute'],
'n_neighbors': [3, 5, 7],
'weights': ['uniform', 'distance']}],
verbose=True)#In[]
print(gs.best_estimator_)
print(gs.best_score_)
print(gs.best_params_)
#Out[]
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm='ball_tree', n_neighbors=7)
0.9800000000000001
{'algorithm': 'ball_tree', 'n_neighbors': 7, 'weights': 'uniform'}시각화를 위한 함수 설정
#In[]
def make_meshgrid(x,y,h=.02):
x_min, x_max = x.min()-1, x.max()+1
y_min, y_max = y.min()-1, y.max()+1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
return xx, yy
def plot_contours(clf, xx, yy, **params):
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
out = plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, **params)
return out#In[]
#저차원 변환
tsne = TSNE(n_components=2)
X_comp = tsne.fit_transform(X)
iris_comp_df = pd.DataFrame(data=X_comp)
iris_comp_df['Target'] = y
iris_comp_df
#Out[]
#In[]
plt.scatter(X_comp[:,0], X_comp[:, 1],
c=y, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, s=20, edgecolors='k')
#Out[]
#In[]
model = KNeighborsClassifier()
model.fit(X_comp, y)
predict = model.predict(X_comp)
xx, yy = make_meshgrid(X_comp[:,0], X_comp[:,1])
plot_contours(model, xx, yy, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, alpha=0.8)
plt.scatter(X_comp[:,0], X_comp[:,1], c=y, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, s=20, edgecolors='k')
#out[]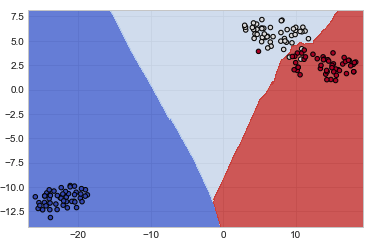
유방암 데이터
#In[]
cancer = load_breast_cancer()
cancer_df = pd.DataFrame(data=cancer.data, columns=cancer.feature_names)
cancer_df['target'] = cancer.target
cancer_df
#Out[]
train data, test data 분리!
#In[]
X, y = cancer.data, cancer.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
cancer_train_df = pd.DataFrame(data=X_train, columns=cancer.feature_names)
cancer_train_df['target'] = y_train
cancer_train_df
#Out[]
#In[]
cancer_test_df = pd.DataFrame(data=X_test, columns=cancer.feature_names)
cancer_test_df['target'] = y_test
cancer_test_df
#Out[]
데이터 전처리 전 점수 / 후 점수
#In[1]
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_scale = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_scale = scaler.transform(X_test)
model = KNeighborsClassifier()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
#Out[1]
#In[2]
print("학습 데이터 점수 : {}".format(model.score(X_train, y_train)))
print("평가 데이터 점수 : {}".format(model.score(X_test, y_test)))
#Out[2]
학습 데이터 점수 : 0.9516483516483516
평가 데이터 점수 : 0.9035087719298246#In[1]
model = KNeighborsClassifier()
model.fit(X_train_scale, y_train)
#Out[1]
KNeighborsClassifier()
#In[2]
print("학습 데이터 점수 : {}".format(model.score(X_train_scale, y_train)))
print("평가 데이터 점수 : {}".format(model.score(X_test_scale, y_test)))
#Out[2]
학습 데이터 점수 : 0.978021978021978
평가 데이터 점수 : 0.9473684210526315모델링
#In[]
estimator = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(),KNeighborsClassifier())
cross_validate(estimator=estimator,
X=X, y=y,
cv=5,
n_jobs=multiprocessing.cpu_count(),
verbose=True)
#Out[]
{'fit_time': array([0.00185204, 0.00381184, 0.00253701, 0.00249338, 0.00242305]),
'score_time': array([0.00689292, 0.01440096, 0.012604 , 0.01277781, 0.01411605]),
'test_score': array([0.96491228, 0.95614035, 0.98245614, 0.95614035, 0.96460177])}#In[]
pipe = Pipeline(
[('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('model', KNeighborsClassifier())])
param_grid = [{'model__n_neighbors' : [3,5,7],
'model__weights' : ['uniform', 'distance'],
'model__algorithm' : ['ball_tree', 'kd_tree', 'brute']}]
gs = GridSearchCV(estimator = pipe,
param_grid = param_grid,
n_jobs=multiprocessing.cpu_count(),
verbose=True)#In[]
gs.fit(X,y)
#Out[]
Fitting 5 folds for each of 18 candidates, totalling 90 fits
Out[64]:
GridSearchCV(estimator=Pipeline(steps=[('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('model', KNeighborsClassifier())]),
n_jobs=4,
param_grid=[{'model__algorithm': ['ball_tree', 'kd_tree', 'brute'],
'model__n_neighbors': [3, 5, 7],
'model__weights': ['uniform', 'distance']}],
verbose=True)#In[]
print(gs.best_estimator_)
print(gs.best_score_)
print(gs.best_params_)
#Out[]
Pipeline(steps=[('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('model',
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm='ball_tree', n_neighbors=7))])
0.9701288619779538
{'model__algorithm': 'ball_tree', 'model__n_neighbors': 7, 'model__weights': 'uniform'}시각화
#In[]
tsne = TSNE(n_components=2)
X_comp = tsne.fit_transform(X)
cancer_comp_df = pd.DataFrame(data=X_comp)
cancer_comp_df['target'] = y
cancer_comp_df
#Out[]
#In[]
plt.scatter(X_comp[:,0], X_comp[:,1], c=y, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, s=20, edgecolors='k')
#Out[]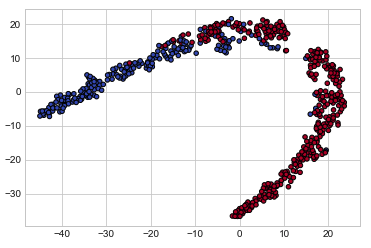
#In[]
model = KNeighborsClassifier()
model.fit(X_comp, y)
predict = model.predict(X_comp)
xx, yy = make_meshgrid(X_comp[:, 0], X_comp[:,1])
plot_contours(model, xx, yy, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, alpha=0.8)
plt.scatter(X_comp[:,0], X_comp[:, 1], c=y, cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, s=20, edgecolors='k')
#Out[]
k 최근접 이웃 회귀
- k 최근접 이웃 분류와 마찬가지로 예측에 이웃 데이터 포인트 사용
- 이웃 데이터 포인트의 평균이 예측 결과
보스턴 주택 가격 데이터
#In[]
boston = load_boston()
boston_df = pd.DataFrame(data=boston.data, columns=boston.feature_names)
boston_df["TARGET"] = boston.target
boston_df
#Out[]
데이터 전처리 전 점수 / 후 점수
#In[1]
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_scale = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_scale = scaler.transform(X_test)
model = KNeighborsRegressor()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
#Out[1]
KNeighborsRegressor()
#In[2]
print("학습 데이터 점수 : {}".format(model.score(X_train, y_train)))
print("평가 데이터 점수 : {}".format(model.score(X_test, y_test)))
#Out[2]
학습 데이터 점수 : 0.6850536552455034
평가 데이터 점수 : 0.44632061414558033#In[1]
model = KNeighborsRegressor()
model.fit(X_train_scale, y_train)
#Out[1]
KNeighborsRegressor()
#In[2]
print("학습 데이터 점수 : {}".format(model.score(X_train_scale, y_train)))
print("평가 데이터 점수 : {}".format(model.score(X_test_scale, y_test)))
#Out[2]
학습 데이터 점수 : 0.8399528467697587
평가 데이터 점수 : 0.7240482286290111모델링
#In[]
estimator = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(),KNeighborsRegressor())
cross_validate(estimator=estimator,
X=X, y=y,
cv=5,
n_jobs=multiprocessing.cpu_count(),
verbose=True)
#Out[]
{'fit_time': array([0.00622606, 0.00805902, 0.00620103, 0.00619411, 0.00268173]),
'score_time': array([0.00342488, 0.00330806, 0.00353193, 0.00340295, 0.00339413]),
'test_score': array([0.56089547, 0.61917359, 0.48661916, 0.46986886, 0.23133037])}#In[]
pipe = Pipeline(
[('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('model', KNeighborsRegressor())])
param_grid = [{'model__n_neighbors' : [3,5,7],
'model__weights' : ['uniform', 'distance'],
'model__algorithm' : ['ball_tree', 'kd_tree', 'brute']}]
gs = GridSearchCV(estimator = pipe,
param_grid = param_grid,
n_jobs=multiprocessing.cpu_count(),
verbose=True)#In[]
gs.fit(X,y)
#Out[]
Fitting 5 folds for each of 18 candidates, totalling 90 fits
Out[110]:
GridSearchCV(estimator=Pipeline(steps=[('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('model', KNeighborsRegressor())]),
n_jobs=4,
param_grid=[{'model__algorithm': ['ball_tree', 'kd_tree', 'brute'],
'model__n_neighbors': [3, 5, 7],
'model__weights': ['uniform', 'distance']}],
verbose=True)#In[]
print(gs.best_estimator_)
print(gs.best_score_)
print(gs.best_params_)
#Out[]
Pipeline(steps=[('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('model',
KNeighborsRegressor(algorithm='ball_tree', n_neighbors=7,
weights='distance'))])
0.4973060611762845
{'model__algorithm': 'ball_tree', 'model__n_neighbors': 7, 'model__weights': 'distance'}시각화
#In[]
tsne = TSNE(n_components=1)
X_comp = tsne.fit_transform(X)
boston_comp_df = pd.DataFrame(data=X_comp)
boston_comp_df['target'] = y
boston_comp_df
#Out[]
#In[]
plt.scatter(X_comp, y, c='b', cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, s=20, edgecolors='k')
#Out[]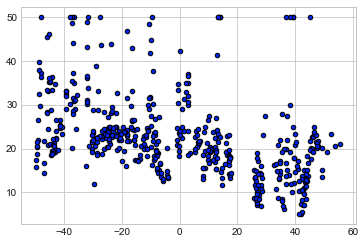
#In[]
model = KNeighborsRegressor()
model.fit(X_comp, y)
predict = model.predict(X_comp)
plt.scatter(X_comp, y, c='b', cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, s=20, edgecolors='k')
plt.scatter(X_comp, predict, c='r', cmap=plt.cm.coolwarm, s=20, edgecolors='k')
#Out[]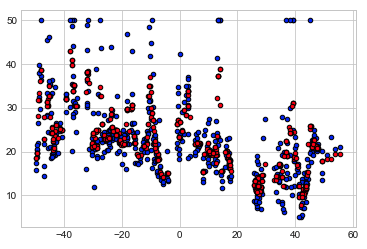
'Youtube > 머신러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [머신러닝] #7 나이브 베이즈 분류 (0) | 2021.12.27 |
|---|---|
| [머신러닝] #5 서포트 벡터 머신 (0) | 2021.12.22 |
| [머신러닝] #4 로지스틱회귀 (0) | 2021.12.21 |
| [머신러닝] #3 선형 모델 Linear Models (0) | 2021.12.20 |
| [머신러닝] #2 Scikits-learn (0) | 2021.12.20 |